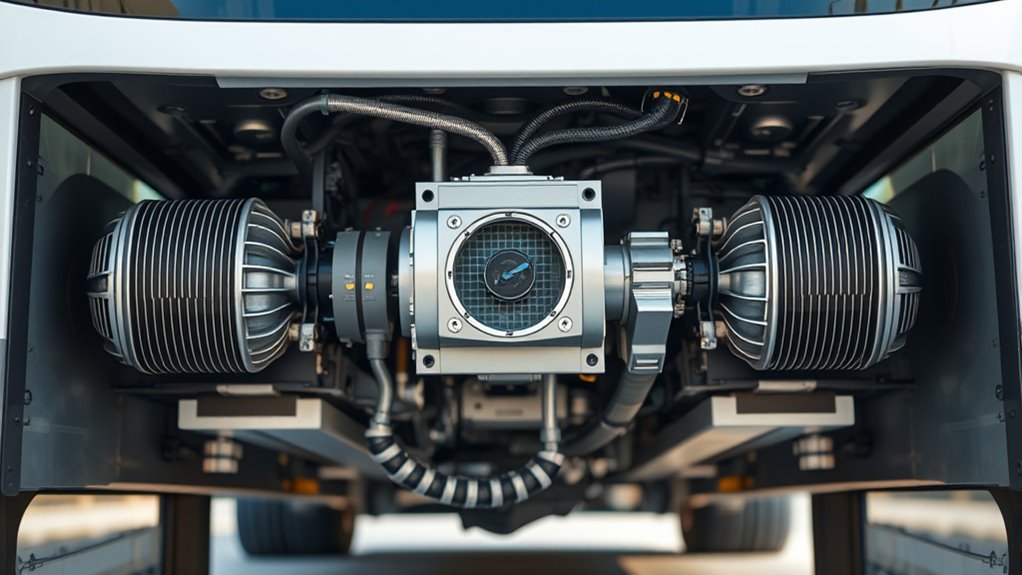
Understanding electric bus powertrains means knowing how electric motors, inverters, and gear ratios work together to provide smooth, efficient performance. The electric motor converts electrical energy into motion, while the inverter controls power delivery by transforming DC to AC and regulating motor speed. Simplified gear ratios help optimize efficiency across various speeds, reducing mechanical complexity. Exploring these components further reveals how they enable reliable, eco-friendly transportation—keep going to uncover more about this innovative technology.
Key Takeaways
- Electric bus motors convert electrical energy into mechanical power, providing instant torque for smooth acceleration and responsive handling.
- The inverter transforms DC from the battery into AC for the motor, regulating power for acceleration, deceleration, and regenerative braking.
- Gear ratios in electric buses are typically fixed, simplifying the drivetrain and optimizing efficiency across diverse driving conditions.
- The Battery Management System (BMS) monitors and controls battery performance to ensure safety, longevity, and optimal energy use.
- Proper integration of motors, inverters, and gear ratios enhances overall efficiency, range, and reliability of the electric bus powertrain.
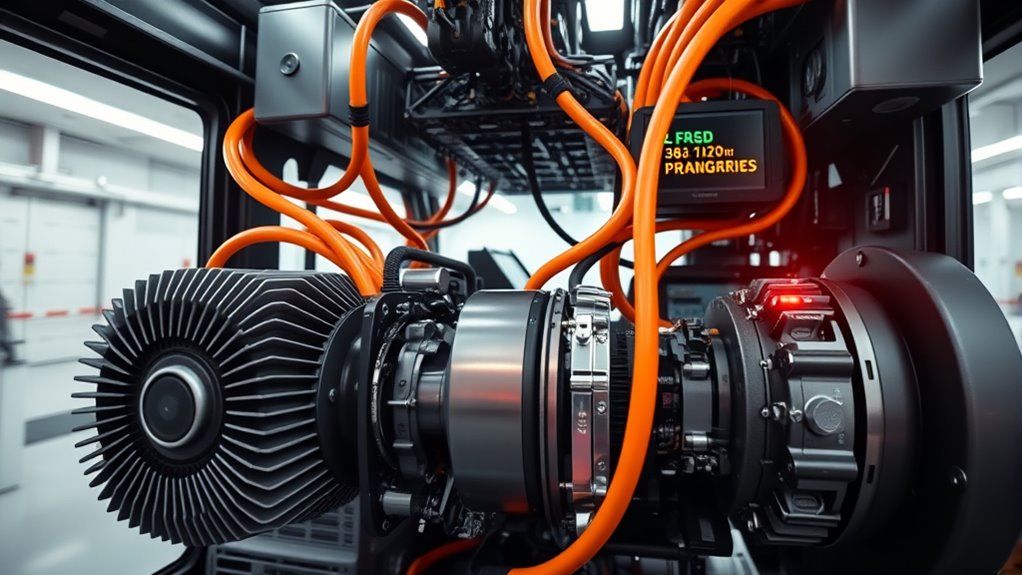
Have you ever wondered how electric buses power their routes silently and efficiently? The secret lies in their sophisticated powertrains, which include advanced battery management systems, powerful motors, and smart control units. The battery management system (BMS) plays a critical role in guaranteeing the longevity and safety of the bus’s large lithium-ion batteries. It monitors voltage, temperature, and state of charge, preventing overcharging or deep discharging that could damage the batteries. By maintaining ideal conditions, the BMS maximizes the battery’s lifespan and performance, allowing the bus to operate reliably over many miles. This system also coordinates with regenerative braking, a feature that recovers energy during deceleration. When you press the brake, instead of wasting kinetic energy as heat, regenerative braking captures that energy and redirects it back into the battery. This process not only extends the driving range but also reduces wear on traditional brake components, making the bus more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Moving on to the core of the powertrain, the electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical power to drive the wheels. These motors are highly efficient, providing instant torque that gives electric buses smooth acceleration and responsive handling. The motor’s output is controlled by an inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) suitable for the motor. The inverter’s precise control of the AC frequency and voltage allows for seamless acceleration, deceleration, and regenerative braking. Together, the motor and inverter work as the heart of the powertrain, delivering power efficiently and reliably. Additionally, the integration of cybersecurity measures in control units ensures the protection of these critical systems from potential digital threats.
Gear ratios also matter considerably in electric bus design. Unlike traditional vehicles that rely on multi-speed transmissions, most electric buses use a fixed gear ratio due to the motor’s broad torque band. This simplifies the drivetrain and reduces mechanical complexity, which in turn lowers maintenance needs. The gear ratio determines how the motor’s rotational speed translates into wheel speed. A well-chosen ratio ensures that the bus operates at peak efficiency across different speeds, providing a smooth ride while conserving energy. When combined with intelligent control systems, these gear ratios help optimize performance whether the bus is cruising on the highway or navigating city streets.
Altogether, understanding how these components work in harmony reveals why electric buses are so effective. Battery management and regenerative braking keep the system efficient and sustainable, while the motor, inverter, and gear ratios work together to deliver power smoothly and reliably. This integration allows electric buses to operate quietly, cleanly, and with minimal downtime, making them a crucial part of modern transportation networks.

P100047 Bus Electric Passenger Door Motor Compatible with Coach & Equipment Buses Replace 113260
Replace Part Number: P100047, 113260, 13260, 21252144, 6092-ECC, 800-171
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Temperature Variations Affect Electric Bus Motor Performance?
Temperature variations directly impact your electric bus motor performance. High ambient temperatures can cause overheating, reducing efficiency and risking damage, while cold temperatures slow down battery thermal management, decreasing power output. You should monitor ambient temperature effects and guarantee proper thermal management systems are in place, maintaining ideal motor temperature. This helps preserve motor efficiency, prolongs component lifespan, and guarantees consistent performance regardless of weather conditions.
What Are the Latest Innovations in Inverter Technology for Buses?
You’ll find that solid state inverters are leading innovations, offering higher efficiency and reliability for buses. They reduce size and weight, making maintenance easier. Additionally, wireless charging technology is advancing, enabling buses to charge seamlessly during stops, increasing operational efficiency. These innovations help optimize power management, extend vehicle range, and reduce downtime, making electric buses more practical and cost-effective for transit agencies.
How Do Gear Ratios Influence Overall Bus Energy Efficiency?
You’re really skating on thin ice if you ignore gear ratio optimization, as it directly impacts your bus’s energy transfer efficiency. Proper gear ratios ensure the motor operates at its most efficient point, reducing energy waste and extending range. When you fine-tune gear ratios for different driving conditions, you maximize energy transfer efficiency, saving power and making your electric bus run smoother and longer on each charge.
What Maintenance Routines Are Recommended for Electric Bus Powertrains?
You should regularly perform battery care by checking for corrosion, maintaining proper charge levels, and avoiding extreme temperatures. Keep up with software updates to optimize powertrain performance and guarantee safety features work correctly. Additionally, inspect electrical connections and cooling systems to prevent overheating and wear. Routine maintenance like these helps extend your electric bus’s lifespan, improves efficiency, and keeps your vehicle running smoothly.
How Do Different Motor Types Compare in Durability and Cost?
You’ll find that AC induction motors generally have a longer motor lifespan and are more durable, making them a reliable choice for electric buses. However, they tend to have higher initial costs. Conversely, permanent magnet motors are often more affordable upfront but may require more maintenance over time, impacting long-term costs. Consider your budget and durability needs when choosing the motor type, balancing initial cost with long-term reliability and maintenance expenses.
electric bus inverter
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve grasped how motors, inverters, and gear ratios work together, imagine your electric bus gliding smoothly through city streets, silent and efficient. Unlike traditional buses with noisy engines and complex transmissions, this modern marvel offers simplicity and eco-friendliness. By understanding these components, you see the future of transportation—quiet, clean, and seamlessly powered. Embrace the shift from the old to the new, where technology drives both progress and sustainability.

Battery Management Systems of Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

Regenerative Braking System of Electric Vehicle Driven by BLDC Motor
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.