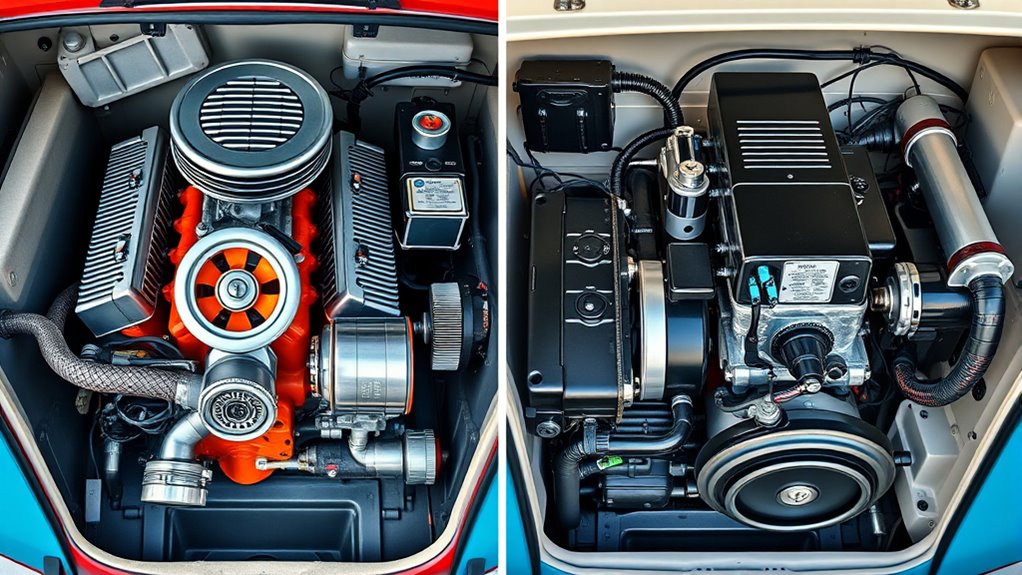
Your VW Bus engine operates differently depending on whether it’s air-cooled or electric. An air-cooled engine uses fins to disperse heat without a radiator or coolant, requiring regular maintenance to keep fins clean and functioning. An electric motor produces less heat and needs simpler cooling, making maintenance easier. As technology advances, electric systems are becoming more efficient and require less upkeep. If you keep exploring, you’ll uncover more about how these systems impact your VW Bus’s performance.
Key Takeaways
- Air-cooled VW engines rely on fins and airflow for heat dissipation, requiring regular fin cleaning and inspection.
- Electric VW motors generate less heat and use simpler thermal management systems, reducing maintenance needs.
- Air-cooled engines need ongoing cooling system upkeep, while electric motors demand minimal upkeep focused on electrical components.
- Proper heat management in both types prevents overheating, but electric motors benefit from advanced cooling technology for longevity.
- Transitioning from air-cooled to electric engines simplifies vehicle maintenance, saving time and costs over the vehicle’s lifespan.

Have you ever wondered how the classic air-cooled engine compares to the modern electric motor in a VW Bus? It’s a fascinating shift in automotive technology, and understanding the differences can help you appreciate how each engine operates and what it takes to keep them running smoothly. With an air-cooled engine, your VW relies on a simple yet effective cooling system that disperses heat through fins on the engine itself. There’s no radiator or coolant involved, which makes the setup straightforward but also means you’ll need to pay close attention to engine maintenance. Over time, the cooling fins can get clogged with dirt or grease, reducing their effectiveness and risking overheating. Regular inspections are essential to guarantee your engine stays cool, especially during hot weather or long drives. You might find yourself cleaning or replacing parts of the cooling system to prevent issues, and knowing how your engine manages heat helps you catch problems early.
In contrast, electric motors in a VW Bus operate with a completely different approach. They generate considerably less heat, thanks to their high efficiency, but they still require some form of thermal management to keep them operating at their best. Instead of a cooling system like a radiator or fins, electric motors often use liquid cooling or air cooling systems designed specifically for their needs. Maintenance for electric motors is generally simpler, focusing more on monitoring electrical components and less on managing heat. You won’t need to worry about engine oil changes or replacing spark plugs; instead, you’ll keep an eye on battery health, electrical connections, and cooling apparatus. Since electric motors produce less heat and don’t have moving parts like pistons or valves, they require less routine maintenance overall, which can save you time and money in the long run. Additionally, advancements in cooling technology continue to improve the efficiency and longevity of electric motors, making them an increasingly popular choice.
The shift from air-cooled to electric engines also changes how you approach vehicle upkeep. While the classic VW Bus demands ongoing attention to its cooling system and engine maintenance, the electric version simplifies many of those tasks. Yet, understanding the basics of how your engine manages heat—whether through fins or liquid cooling—remains vital. Proper maintenance guarantees your VW runs efficiently and prevents costly repairs down the line. Whether you’re preserving the vintage charm of a classic air-cooled engine or enjoying the low-maintenance benefits of an electric motor, knowing how each system operates helps you keep your VW Bus in top shape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Air-Cooled VW Engines Compare to Modern Liquid-Cooled Engines?
You might notice that air-cooled VW engines rely on cooling systems that use airflow and fins, unlike modern liquid-cooled engines that circulate coolant. While air-cooled engines are simpler and easier to maintain, they typically don’t last as long as liquid-cooled ones. Liquid cooling helps control engine temperature more effectively, which can improve engine longevity and performance, especially under heavy or prolonged use.
What Are the Maintenance Differences Between Air-Cooled and Electric VW Engines?
Maintenance might seem manageable, but it differs considerably. With cooling maintenance, you’ll check and replace oil regularly in air-cooled engines, ensuring proper heat management. Electric engines, however, demand minimal cooling attention, with no oil changes needed. You avoid oily messes and oil requirements altogether, making upkeep simpler and cleaner. So, while air-cooled engines require routine oil and cooling checks, electric engines offer easier, cleaner maintenance, saving you time and effort.
How Does Engine Noise Differ Between Air-Cooled and Electric VW Buses?
You’ll notice that engine sound and noise levels differ markedly between air-cooled and electric VW buses. With an air-cooled engine, you hear a distinctive, consistent hum and occasional rattling that gives it character. In contrast, electric buses are much quieter, producing minimal noise, mostly just the sounds of wind and tires. This quieter operation creates a more peaceful ride, while the air-cooled engine offers a nostalgic, lively auditory experience.
What Is the Environmental Impact of Each Engine Type?
They say “every choice has a consequence,” and that’s true for engine types. Electric engines produce fewer emissions and have a smaller emissions footprint, but face recycling challenges due to battery disposal. Air-cooled engines emit more pollutants and are harder on the environment overall. You’ll want to weigh these impacts when choosing, knowing that electric options may be better long-term, despite current recycling hurdles.
Can a VW Bus Be Converted From Air-Cooled to Electric?
You can convert your VW Bus from air-cooled to electric, but it’s a vintage modification that involves significant conversion challenges. You’ll need to replace the engine, install batteries, and modify the drivetrain, which requires technical skill and patience. While it’s feasible, expect a complex project that may affect the bus’s originality. Carefully research and consider professional help to guarantee a successful electric conversion that preserves your classic vehicle’s charm.
Conclusion
So, whether you prefer the classic charm of an air-cooled engine or the modern efficiency of an electric conversion, remember it’s all about what suits your lifestyle. Some worry electric isn’t as authentic, but with advancements, you get smooth, quiet rides without sacrificing the VW spirit. Don’t let the nostalgia hold you back—embrace the future while keeping that iconic VW vibe alive. Your perfect bus experience is just a decision away.